Connect to Amazon OpenSearch for search and aggregate queries
Amazon OpenSearch Service provides a managed platform for deploying search and analytics solutions with OpenSearch or Elasticsearch. The zero-ETL integration between Amazon DynamoDB and OpenSearch Service allows seamless search on DynamoDB data by automatically replicating and transforming it without requiring custom code or infrastructure. This integration simplifies processes and reduces the operational workload of managing data pipelines.
DynamoDB users gain access to advanced OpenSearch features like full-text search, fuzzy search, auto-complete, and vector search for machine learning capabilities. Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion synchronizes data between DynamoDB and OpenSearch Service, enabling near-instant updates and comprehensive insights across multiple DynamoDB tables. Developers can adjust index mapping templates to match Amazon DynamoDB fields with OpenSearch Service indexes.
Amazon OpenSearch Ingestion, combined with S3 exports and DynamoDB streams, facilitates seamless data input from DynamoDB tables and automatic ingestion into OpenSearch. Additionally, the pipeline can back up data to S3 for potential future re-ingestion as needed.
Step 1: Setup the project
Begin by setting up your project by following the instructions in the Quickstart guide. For the purpose of this guide, we'll sync a Todo table from DynamoDB to OpenSearch.
Firstly, add the Todo model to your schema:
import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Todo: a .model({ content: a.string(), done: a.boolean(), priority: a.enum(["low", "medium", "high"]), }) .authorization((allow) => [allow.publicApiKey()])});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: "apiKey", apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});import * as dynamodb from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';import { defineBackend } from '@aws-amplify/backend';import { auth } from './auth/resource';import { data } from './data/resource';
const backend = defineBackend({ auth, data});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables['Todo'];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables['Todo'].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables['Todo'].tableName;Step 2: Setting Up the OpenSearch Instance
Create an OpenSearch instance with encryption.
import * as opensearch from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-opensearchservice';import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib";import { defineBackend } from '@aws-amplify/backend';import { auth } from './auth/resource';import { data } from './data/resource';
const backend = defineBackend({ auth, data});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables['Todo'];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables['Todo'].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables['Todo'].tableName;
// Create the OpenSearch domainconst openSearchDomain = new opensearch.Domain( backend.data.stack, 'OpenSearchDomain', { version: opensearch.EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_2_11, capacity: { // upgrade instance types for production use masterNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", masterNodes: 0, dataNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", dataNodes: 1, }, nodeToNodeEncryption: true, // set removalPolicy to DESTROY to make sure the OpenSearch domain is deleted on stack deletion. removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, encryptionAtRest: { enabled: true } });Step 3: Setting Up Zero ETL from DynamoDB to OpenSearch
Step 3a: Setup Storage and IAM Role
Establish Storage to back up raw events consumed by the OpenSearch pipeline.
Generate a file named amplify/storage/resource.ts and insert the provided content to set up a storage resource. Tailor your storage configurations to regulate access to different paths within your storage bucket.
import { defineStorage } from "@aws-amplify/backend"
export const storage = defineStorage({ name: "opensearch-backup-bucket-amplify-gen-2", access: allow => ({ 'public/*': [ allow.guest.to(['list', 'write', 'get']) ] })})Get the s3BucketArn and s3BucketName values from storage resource as shown below. Additionally, configure an IAM role for the pipeline and assign the roles as indicated below. For further information on the required IAM roles, please refer to the Setting up roles and users documentation.
import * as dynamodb from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb";import * as opensearch from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-opensearchservice";import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib";import * as iam from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam";import { defineBackend } from "@aws-amplify/backend";import { auth } from "./auth/resource";import { data } from "./data/resource";import { storage } from "./storage/resource";
// Define backend resourcesconst backend = defineBackend({ auth, data, storage,});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables["Todo"];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE,};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableName;
// Create the OpenSearch domainconst openSearchDomain = new opensearch.Domain( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchDomain", { version: opensearch.EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_2_11, capacity: { // upgrade instance types for production use masterNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", masterNodes: 0, dataNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", dataNodes: 1, }, nodeToNodeEncryption: true, // set removalPolicy to DESTROY to make sure the OpenSearch domain is deleted on stack deletion. removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, encryptionAtRest: { enabled: true, }, });// Get the S3Bucket ARNconst s3BucketArn = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketArn;// Get the S3Bucket Nameconst s3BucketName = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketName;
// Create an IAM role for OpenSearch integrationconst openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole = new iam.Role( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchIntegrationPipelineRole", { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("osis-pipelines.amazonaws.com"), inlinePolicies: { openSearchPipelinePolicy: new iam.PolicyDocument({ statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:DescribeDomain"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:ESHttp*"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:AbortMultipartUpload", "s3:PutObject", "s3:PutObjectAcl", ], resources: [s3BucketArn, s3BucketArn + "/*"], }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "dynamodb:DescribeTable", "dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups", "dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime", "dynamodb:DescribeExport", "dynamodb:DescribeStream", "dynamodb:GetRecords", "dynamodb:GetShardIterator", ], resources: [tableArn, tableArn + "/*"], }), ], }), }, managedPolicies: [ iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( "AmazonOpenSearchIngestionFullAccess" ), ], });For the S3 bucket, follow standard security practices: block public access, encrypt data at rest, and enable versioning.
The IAM role should allow the OpenSearch Ingestion Service (OSIS) pipelines to assume it. Grant specific OpenSearch Service permissions and also provide DynamoDB and S3 access. You may customize permissions to follow the principle of least privilege.
Step 3b: OpenSearch Service Pipeline
Define the pipeline construct and its configuration.
When using OpenSearch, you can define the index template or mapping in advance based on your data structure, which allows you to set data types for each field in the document. This approach can be incredibly powerful for precise data ingestion and search. For more information on index mapping/templates, please refer to OpenSearch documentation.
Customize the template_content JSON-representation to define the data structure for the ingestion pipeline.
import * as dynamodb from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb";import * as opensearch from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-opensearchservice";import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib";import * as iam from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam";import { defineBackend } from "@aws-amplify/backend";import { auth } from "./auth/resource";import { data } from "./data/resource";import { storage } from "./storage/resource"; // Define backend resourcesconst backend = defineBackend({ auth, data, storage,});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables["Todo"];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE,};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableName;
// Create the OpenSearch domainconst openSearchDomain = new opensearch.Domain( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchDomain", { version: opensearch.EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_2_11, capacity: { // upgrade instance types for production use masterNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", masterNodes: 0, dataNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", dataNodes: 1, }, nodeToNodeEncryption: true, // set removalPolicy to DESTROY to make sure the OpenSearch domain is deleted on stack deletion. removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, encryptionAtRest: { enabled: true, }, });
// Get the S3Bucket ARNconst s3BucketArn = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketArn;// Get the S3Bucket Nameconst s3BucketName = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketName;
// Create an IAM role for OpenSearch integrationconst openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole = new iam.Role( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchIntegrationPipelineRole", { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("osis-pipelines.amazonaws.com"), inlinePolicies: { openSearchPipelinePolicy: new iam.PolicyDocument({ statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:DescribeDomain"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:ESHttp*"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:AbortMultipartUpload", "s3:PutObject", "s3:PutObjectAcl", ], resources: [s3BucketArn, s3BucketArn + "/*"], }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "dynamodb:DescribeTable", "dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups", "dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime", "dynamodb:DescribeExport", "dynamodb:DescribeStream", "dynamodb:GetRecords", "dynamodb:GetShardIterator", ], resources: [tableArn, tableArn + "/*"], }), ], }), }, managedPolicies: [ iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( "AmazonOpenSearchIngestionFullAccess" ), ], });
// Define OpenSearch index mappingsconst indexName = "todo";
const indexMapping = { settings: { number_of_shards: 1, number_of_replicas: 0, }, mappings: { properties: { id: { type: "keyword", }, done: { type: "boolean", }, content: { type: "text", }, }, },};The configuration is a data-prepper feature of OpenSearch. For specific documentation on DynamoDB configuration, refer to OpenSearch data-prepper documentation.
import * as dynamodb from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb";import * as opensearch from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-opensearchservice";import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib";import * as iam from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam";import { defineBackend } from "@aws-amplify/backend";import { auth } from "./auth/resource";import { data } from "./data/resource";import { storage } from "./storage/resource"; // Define backend resourcesconst backend = defineBackend({ auth, data, storage,});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables["Todo"];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE,};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableName;
// Create the OpenSearch domainconst openSearchDomain = new opensearch.Domain( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchDomain", { version: opensearch.EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_2_11, capacity: { // upgrade instance types for production use masterNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", masterNodes: 0, dataNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", dataNodes: 1, }, nodeToNodeEncryption: true, // set removalPolicy to DESTROY to make sure the OpenSearch domain is deleted on stack deletion. removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, encryptionAtRest: { enabled: true, }, });
// Get the S3Bucket ARNconst s3BucketArn = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketArn;// Get the S3Bucket Nameconst s3BucketName = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketName;
// Create an IAM role for OpenSearch integrationconst openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole = new iam.Role( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchIntegrationPipelineRole", { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("osis-pipelines.amazonaws.com"), inlinePolicies: { openSearchPipelinePolicy: new iam.PolicyDocument({ statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:DescribeDomain"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:ESHttp*"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:AbortMultipartUpload", "s3:PutObject", "s3:PutObjectAcl", ], resources: [s3BucketArn, s3BucketArn + "/*"], }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "dynamodb:DescribeTable", "dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups", "dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime", "dynamodb:DescribeExport", "dynamodb:DescribeStream", "dynamodb:GetRecords", "dynamodb:GetShardIterator", ], resources: [tableArn, tableArn + "/*"], }), ], }), }, managedPolicies: [ iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( "AmazonOpenSearchIngestionFullAccess" ), ], });
// Define OpenSearch index mappingsconst indexName = "todo";
const indexMapping = { settings: { number_of_shards: 1, number_of_replicas: 0, }, mappings: { properties: { id: { type: "keyword", }, isDone: { type: "boolean", }, content: { type: "text", }, priority: { type: "text", }, }, },};
// OpenSearch template definitionconst openSearchTemplate = `version: "2"dynamodb-pipeline: source: dynamodb: acknowledgments: true tables: - table_arn: "${tableArn}" stream: start_position: "LATEST" export: s3_bucket: "${s3BucketName}" s3_region: "${backend.storage.stack.region}" s3_prefix: "${tableName}/" aws: sts_role_arn: "${openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole.roleArn}" region: "${backend.data.stack.region}" sink: - opensearch: hosts: - "https://${openSearchDomain.domainEndpoint}" index: "${indexName}" index_type: "custom" template_content: | ${JSON.stringify(indexMapping)} document_id: '\${getMetadata("primary_key")}' action: '\${getMetadata("opensearch_action")}' document_version: '\${getMetadata("document_version")}' document_version_type: "external" bulk_size: 4 aws: sts_role_arn: "${openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole.roleArn}" region: "${backend.data.stack.region}"`;This configuration defines the desired behavior of the pipeline for a single model.
In the source configuration, DynamoDB is specified as the data source, along with the target table for ingestion and the starting point of the stream. Additionally, besides ingesting the stream into OpenSearch, a target S3 bucket is defined for backup purposes. Furthermore, an IAM role is set for the ingestion pipeline, ensuring it possesses the necessary permissions and policies as detailed in the documentation.
Regarding the sink configuration, the OpenSearch domain cluster is specified by setting the host, index name, type, and template content (index mapping) for data formatting. Document-related metadata is configured along with the maximum bulk size for requests to OpenSearch in MB. Once again, an IAM role is specified for the sink portion of the pipeline. For further details on Sink configuration, please refer to the OpenSearch documentation.
The sink configuration is an array. To create a different index on the same table, you can achieve this by adding a second OpenSearch configuration to the sink array.
To index multiple tables, you'll need to configure multiple pipelines in the configuration. For further guidance, please consult the pipeline section of the OpenSearch documentation.
Now, create the OSIS pipeline resource:
import * as dynamodb from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb";import * as opensearch from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-opensearchservice";import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib";import * as iam from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam";import * as osis from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-osis";import * as logs from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-logs";import { RemovalPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib"; import { defineBackend } from "@aws-amplify/backend";import { auth } from "./auth/resource";import { data } from "./data/resource";import { storage } from "./storage/resource";
// Define backend resourcesconst backend = defineBackend({ auth, data, storage,});
const todoTable = backend.data.resources.cfnResources.amplifyDynamoDbTables["Todo"];
// Update table settingstodoTable.pointInTimeRecoveryEnabled = true;
todoTable.streamSpecification = { streamViewType: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_IMAGE,};
// Get the DynamoDB table ARNconst tableArn = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableArn;// Get the DynamoDB table nameconst tableName = backend.data.resources.tables["Todo"].tableName;
// Create the OpenSearch domainconst openSearchDomain = new opensearch.Domain( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchDomain", { version: opensearch.EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_2_11, capacity: { // upgrade instance types for production use masterNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", masterNodes: 0, dataNodeInstanceType: "t3.small.search", dataNodes: 1, }, nodeToNodeEncryption: true, // set removalPolicy to DESTROY to make sure the OpenSearch domain is deleted on stack deletion. removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, encryptionAtRest: { enabled: true, }, });
// Get the S3Bucket ARNconst s3BucketArn = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketArn;// Get the S3Bucket Nameconst s3BucketName = backend.storage.resources.bucket.bucketName;
// Create an IAM role for OpenSearch integrationconst openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole = new iam.Role( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchIntegrationPipelineRole", { assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("osis-pipelines.amazonaws.com"), inlinePolicies: { openSearchPipelinePolicy: new iam.PolicyDocument({ statements: [ new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:DescribeDomain"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ actions: ["es:ESHttp*"], resources: [ openSearchDomain.domainArn, openSearchDomain.domainArn + "/*", ], effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:AbortMultipartUpload", "s3:PutObject", "s3:PutObjectAcl", ], resources: [s3BucketArn, s3BucketArn + "/*"], }), new iam.PolicyStatement({ effect: iam.Effect.ALLOW, actions: [ "dynamodb:DescribeTable", "dynamodb:DescribeContinuousBackups", "dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime", "dynamodb:DescribeExport", "dynamodb:DescribeStream", "dynamodb:GetRecords", "dynamodb:GetShardIterator", ], resources: [tableArn, tableArn + "/*"], }), ], }), }, managedPolicies: [ iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName( "AmazonOpenSearchIngestionFullAccess" ), ], });
// Define OpenSearch index mappingsconst indexName = "todo";
const indexMapping = { settings: { number_of_shards: 1, number_of_replicas: 0, }, mappings: { properties: { id: { type: "keyword", }, isDone: { type: "boolean", }, content: { type: "text", }, priority: { type: "text", }, }, },};
// OpenSearch template definitionconst openSearchTemplate = `version: "2"dynamodb-pipeline: source: dynamodb: acknowledgments: true tables: - table_arn: "${tableArn}" stream: start_position: "LATEST" export: s3_bucket: "${s3BucketName}" s3_region: "${backend.storage.stack.region}" s3_prefix: "${tableName}/" aws: sts_role_arn: "${openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole.roleArn}" region: "${backend.data.stack.region}" sink: - opensearch: hosts: - "https://${openSearchDomain.domainEndpoint}" index: "${indexName}" index_type: "custom" template_content: | ${JSON.stringify(indexMapping)} document_id: '\${getMetadata("primary_key")}' action: '\${getMetadata("opensearch_action")}' document_version: '\${getMetadata("document_version")}' document_version_type: "external" bulk_size: 4 aws: sts_role_arn: "${openSearchIntegrationPipelineRole.roleArn}" region: "${backend.data.stack.region}"`;
// Create a CloudWatch log groupconst logGroup = new logs.LogGroup(backend.data.stack, "LogGroup", { logGroupName: "/aws/vendedlogs/OpenSearchService/pipelines/1", removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,});
// Create an OpenSearch Integration Service pipelineconst cfnPipeline = new osis.CfnPipeline( backend.data.stack, "OpenSearchIntegrationPipeline", { maxUnits: 4, minUnits: 1, pipelineConfigurationBody: openSearchTemplate, pipelineName: "dynamodb-integration-2", logPublishingOptions: { isLoggingEnabled: true, cloudWatchLogDestination: { logGroup: logGroup.logGroupName, }, }, });After deploying the resources, you can test the data ingestion process by adding an item to the Todo table. However, before doing that, let's verify that the pipeline has been set up correctly.
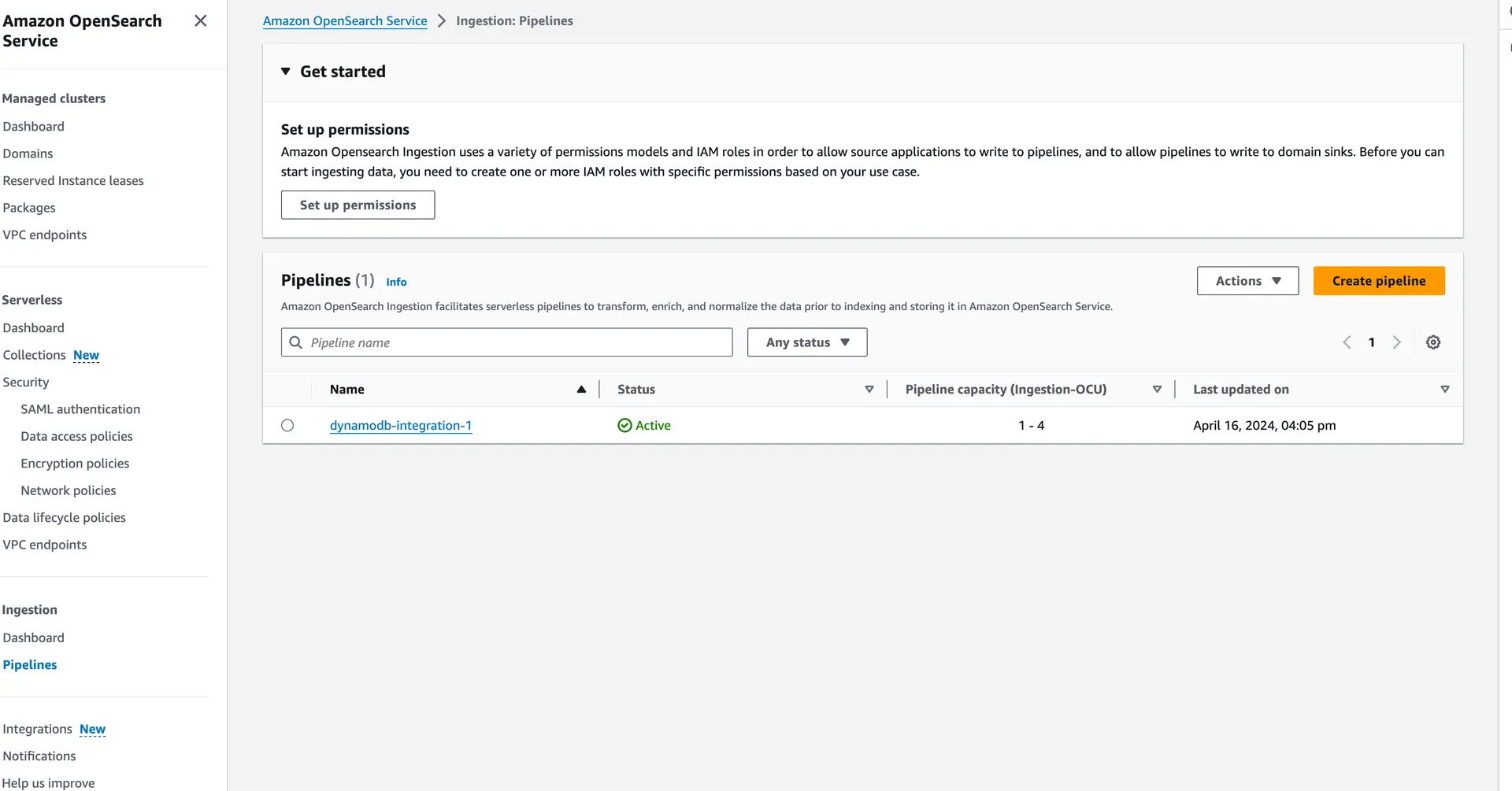
In the AWS console, navigate to OpenSearch and then to the pipelines section. You should find your configured pipeline and review its settings to ensure they match your expectations:
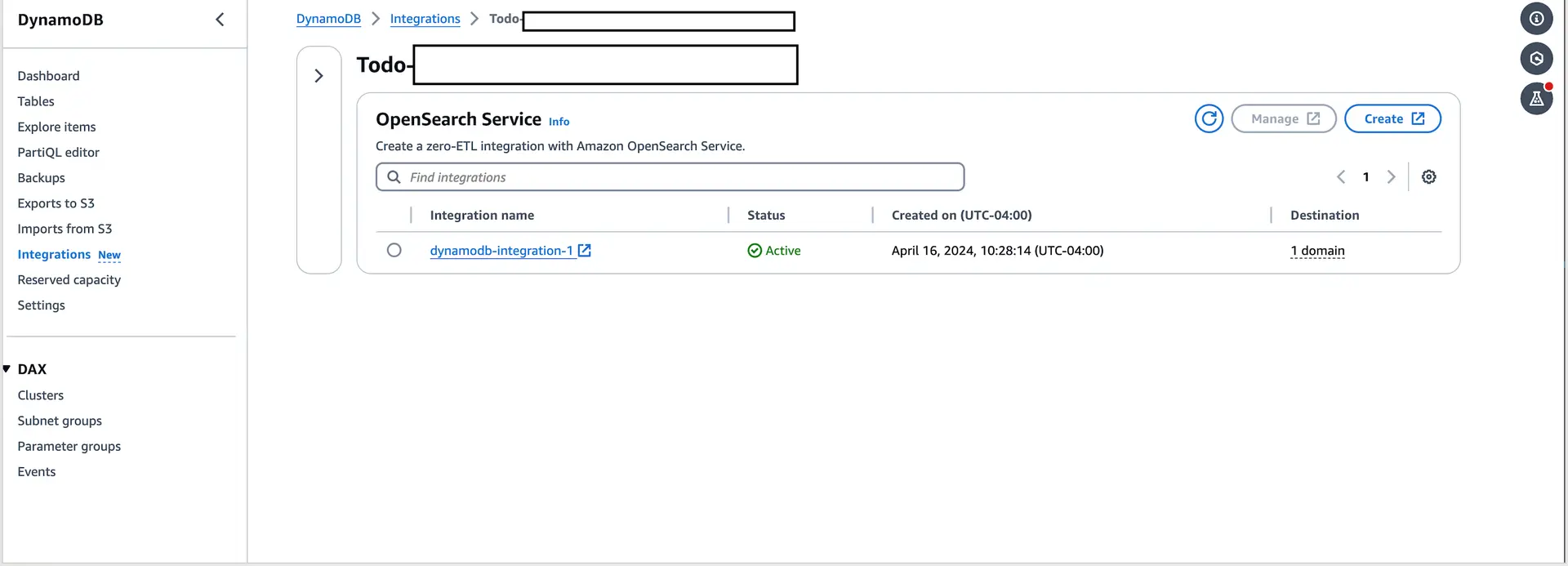
You can also check this in the DynamoDB console by going to the Integrations section of the tables.
Step 4: Expose new queries on OpenSearch
Step 4a: Add OpenSearch Datasource to backend
First, Add the OpenSearch data source to the data backend. Add the following code to the end of the amplify/backend.ts file.
// Add OpenSearch data source const osDataSource = backend.data.addOpenSearchDataSource( "osDataSource", openSearchDomain);Step 4b: Create Resolver and attach to query
Let's create the search resolver. Create a new file named amplify/data/searchTodoResolver.js and paste the following code. For additional details please refer to Amazon OpenSearch Service Resolvers
import { util } from "@aws-appsync/utils";
/** * Searches for documents by using an input term * @param {import('@aws-appsync/utils').Context} ctx the context * @returns {*} the request */export function request(ctx) { return { operation: "GET", path: "/todo/_search", };}
/** * Returns the fetched items * @param {import('@aws-appsync/utils').Context} ctx the context * @returns {*} the result */export function response(ctx) { if (ctx.error) { util.error(ctx.error.message, ctx.error.type); } return ctx.result.hits.hits.map((hit) => hit._source);}Step 4c: Add the AppSync Resolver for the Search Query
Update the schema and add a searchTodo query.
const schema = a.schema({ Todo: a .model({ content: a.string(), done: a.boolean(), priority: a.enum(["low", "medium", "high"]), }) .authorization((allow) => [allow.publicApiKey()]),
searchTodos: a .query() .returns(a.ref("Todo").array()) .authorization((allow) => [allow.publicApiKey()]) .handler( a.handler.custom({ entry: "./searchTodoResolver.js", dataSource: "osDataSource", }) ),
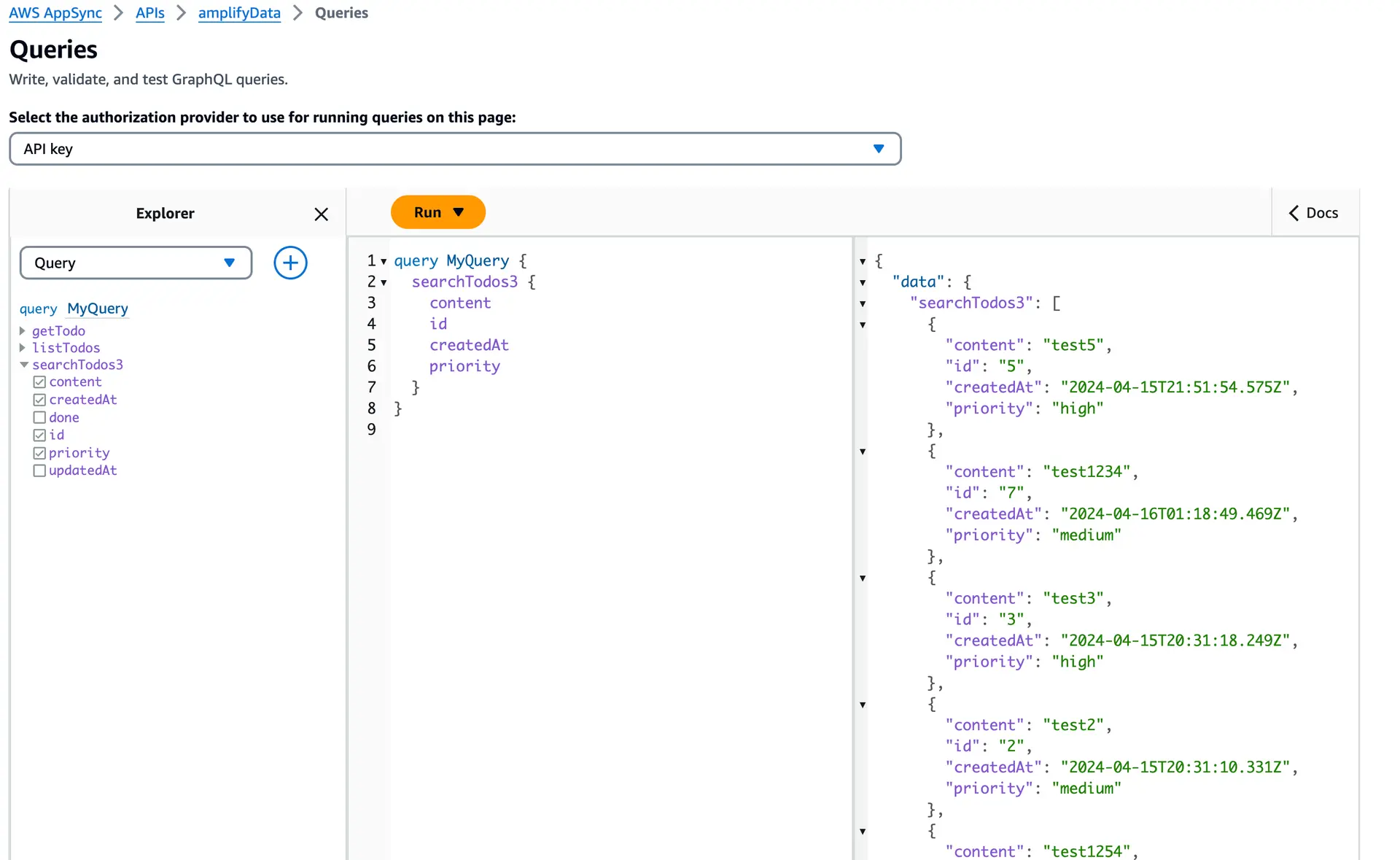
});Once you've deployed the resources, you can verify the changes by checking the AppSync console. Run the 'searchTodo' query and review the results to confirm their accuracy.