Configure special inputs
Autocomplete fields with relationships
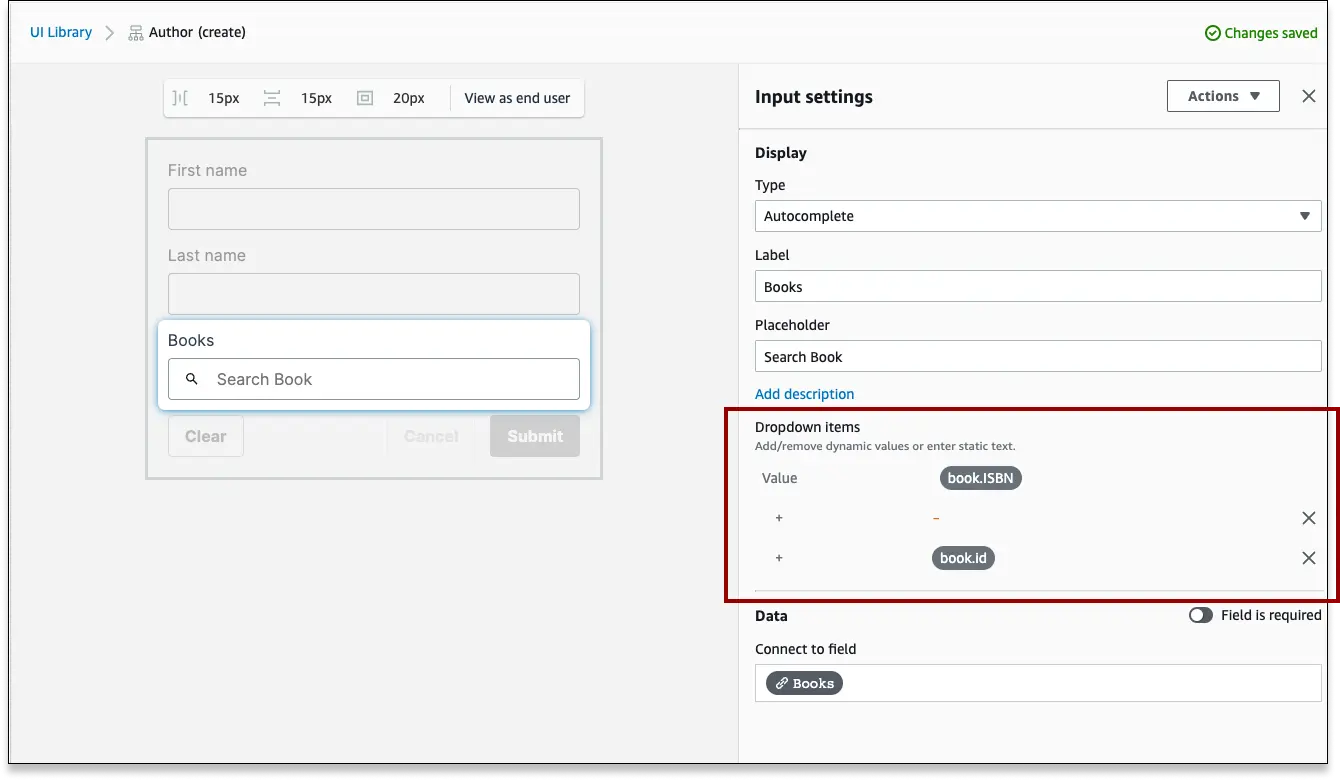
If you have a Connected Form bound to a data model with relationships, Form Builder uses a special field to handle submission. The Autocomplete field will allow your form submitters to select one or more records from a related data model. These connected autocomplete fields have some special configuration settings.
Form builder now supports data binding to GraphQL APIs without Conflict Resolution. Learn more about GraphQL and Conflict Resolution here.
Activate relationship fields in forms
If you have relationships in your data models, but your connected forms are missing related fields, Relationship fields may not be activated. To turn on relationships support...
- Log into your Studio application
- On the left-hand bar, select UI Library
- In the upper right-hand corner, select UI Library settings
- Select Relationship fields to activate
Customize record labels
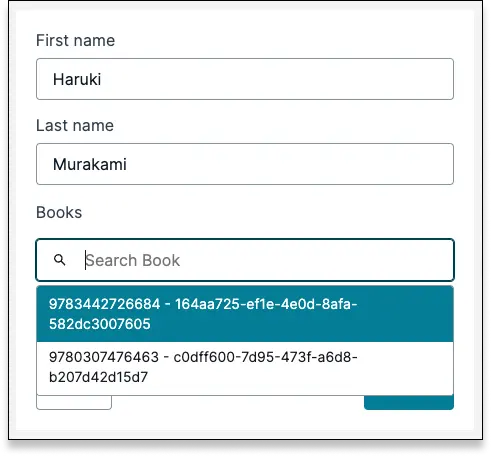
When a form submitter selects an autocomplete field in your form, it will be populated with a list of related records. By default, these records will be labeled with the first field in the data model, a hyphen, and the record's ID.
In this example, the form creates a new author, and lets the user look up the related book. The first field in the Book model is ISBN, so the label displays as:
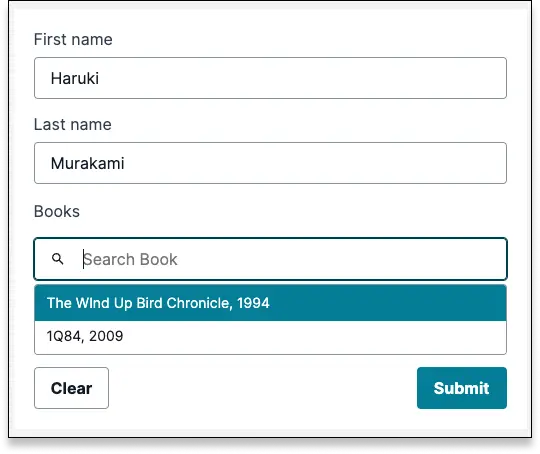
To make this more useful for the form submitter, you can customize the label with any fields in the model, and string concatenation. In this example, the book's name field, a comma, and the year field makes more sense.
Using forms with relationships in code
When you are satisfied with your form configuration and style, your forms can be generated in your local project.
If your GraphQL API is not using DataStore, forms with relationships require a query codegen depth of 4, and will not work as expected otherwise. To update your query depth:
- Open your terminal and navigate to the root directory of your Amplify project
- Run
amplify configure codegen - When prompted for Query Depth, change to 4. All other options can be set as you prefer
- After confirming all settings, run
amplify codegento update query generation in your project
File Uploader
File Uploader fields allow your forms to accept file uploads, which are stored in an Amazon S3 bucket connected to your Amplify app. After uploading, that file's S3 key is stored in your data model, allowing for systematic retrieval using the Amplify JS library.
Prerequisites
In order to use the File Uploader field, your Amplify app must meet some prerequisites:
- You must have an Amplify app with Studio enabled
- You must have Amplify Authentication, either through Studio or through the CLI
- You must have added Amplify Storage to your app, either through Studio or through the CLI
How it works
The File Uploader input in Form Builder will allow the form submitter to select from files on their local device and upload them to an S3 bucket. File Uploader automatically connects to your S3 bucket added as part of Amplify Storage, and uses the same File level access concepts, defaulting to private.
Files are uploaded immediately upon selection, and an S3 key is generated. By default, File Uploader will generate a unique S3 key based on the file uploaded. On form submission, File Uploader will return the S3 key of the uploaded file as a String.
If your File Uploader field is connected to a field in your data model, the S3 key will be written to your database via your GraphQL API. If the field is not connected to a data model, you can handle the S3 key manually with the onSubmit hook.
File Uploader with connected forms
If a File Uploader field is bound to a data model as part of a connected form, a record is created or updated in the bound data model when the form is submitted.
When a File Uploader input field is added to a connected form, the S3 key of the uploaded file is written to a String field in the connected data model.
Prerequisites:
- You must have a GraphQL API, deployed either through Studio or through the CLI.
- You must have at least one field in your data model with a type of
String - You must have a connected form. This can be a default form, or a custom connected form
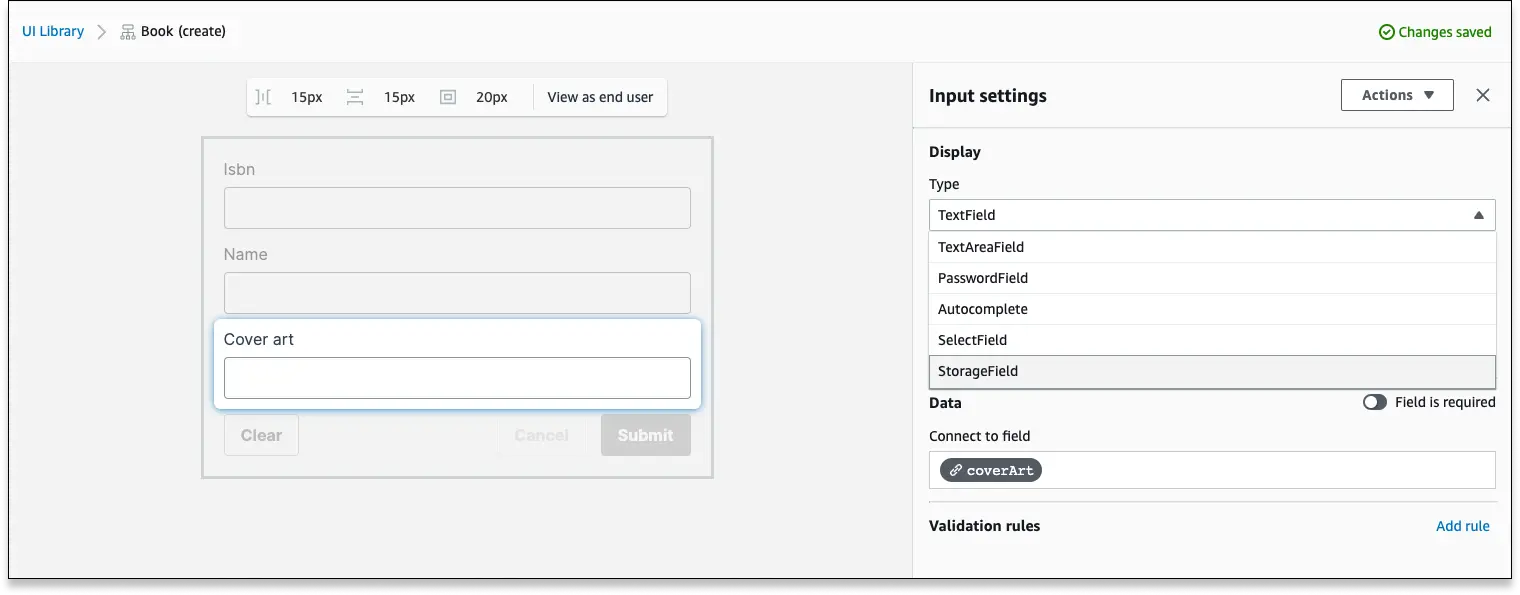
Add File Uploader to a connected form...
- Log into your Studio app and select the UI Library
- Select a connected form and select Configure in the upper right-hand corner
- Select the
stringfield you would like to convert to a File Uploader field - In the Display section of the Input settings sidebar, select the Type dropdown and choose
StorageField
File Uploader with unconnected forms
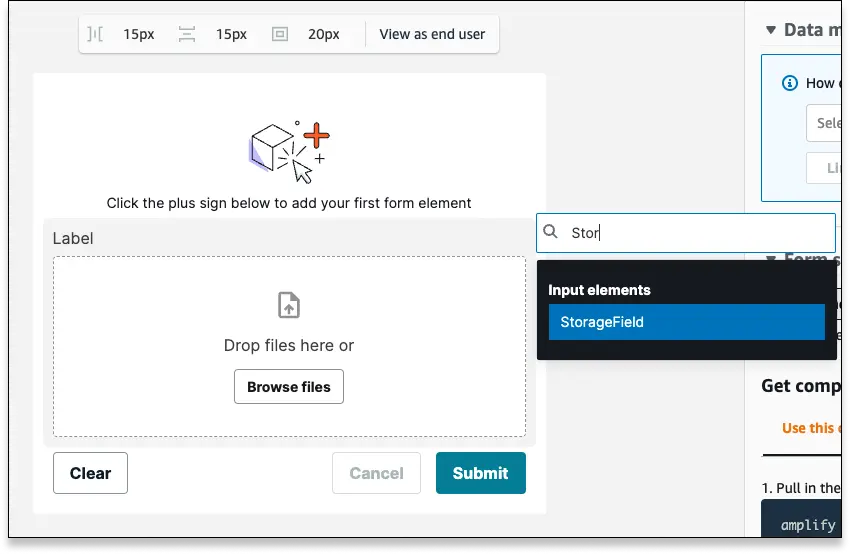
Add a File Uploader field to an unconnected form...
- Log into your Studio app and select the UI Library
- Navigate to an unconnected form, or create a new blank form
- Click the blue plus sign to add a new field to your form
- Select a
StorageFieldinput element
With all unconnected forms, the form submission must be configured manually. Use the onSubmit hook and the fields object to handle submission in code.
Configuring File Uploader
File Uploader has several unique configurations that can be applied in the right-hand toolbar.
- File level access: determines which users can access the uploaded file. File Uploader will default to Private.
- Private: only accessible to the uploader
- Protected: accessible to any authenticated user
- Public: accessible to anyone
- Accepted file types: limits which file types can be uploaded
- Advanced settings
- Maximum number of files: max number of files that can be added to the form before submission. If your bound data model field is not an array, this will always be 1
- Maximum file size: max size for each file uploaded
- Is pausable: allows the user to pause and resume the upload
- Preview image: if the uploaded file is an image, a preview of the image will be rendered in your form
File level access
File Uploader uses the same File level access concepts as the Storage category, defaulting to private. If you select private or protected file level access, all files uploaded will have {user_identity_id} in the file path. This restricts Read and Write access, and ensures identical files uploaded by different users have unique paths.
Unique S3 keys
If files with identical S3 keys are uploaded to the same path, S3 will overwrite those files. To prevent accidental overwriting of files, File Uploader generates a unique S3 key by hashing the file contents. Uploading different files with the same name will not overwrite the original file.
However, if a form submitter uploads two identical files to the same path - even with different file names - File Uploader will prevent file duplication in your S3 bucket.