Manage MFA settings
The Auth category supports Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) for user sign-in flows. MFA is an extra layer of security used to make sure that users trying to gain access to an account are who they say they are. It requires users to provide additional information to verify their identity. Amplify Auth supports the MFA methods with Time-based-One-Time Passwords (TOTP) as well as text messages (SMS). In this guide we will review how you can set up MFA using TOTP and SMS and the tradeoffs between these methods to help you choose the right set up for your application. We’ll also review how to set up MFA to remember a device and reduce sign-in friction for your users.
Before you begin, you will need:
- The Amplify libraries installed and configured
- Optional If you are using SMS you will need a phone number provisioned with an SNS/Pinpoint
Enable multi-factor authentication
Below are the steps you can use to set up MFA using SMS or TOTP with the Amplify CLI. The Amplify libraries are designed to work with MFA even if you have set up your Amazon Cognito resources separately.
Understand your MFA options
When enabling MFA you will have two key decisions to make:
- MFA enforcement: As part of this setup you will determine how MFA is enforced. If you require MFA by setting MFA login to "ON", all your users will need to complete MFA to sign in. If you keep it "Optional", your users will have the choice whether to enable MFA or not for their account.
- MFA methods: You will also specify which MFA method you are using - TOTP (Time-based One-time Password), SMS (text message), or both. We recommend that you use TOTP-based MFA as it is more secure and you can reserve SMS for account recovery.
Learn moreCompare TOTP and SMS MFA methods
| Time-based One-time Password (TOTP) | Short Message Service (SMS) | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Generates a short-lived numeric code for user authentication that includes a shared secret key and current time using an authenticator app. | Generates a one-time code shared via text message that is entered with other credentials for user authentication. |
| Benefits | More secure than SMS since the code is generated locally and not transmitted over a network. TOTP also works without cell service as long as the TOTP app is installed. | Easy to set up with a user-provided phone number and is familiar to users as a common authentication method. |
| Constraints | Requires an app to generate codes and adds to the initial setup of an account. Codes also expire quickly and must be used promptly after it is generated. | SMS requires cell service and can include an additional cost for the user. Although rare, SMS messages can also be intercepted. |
Enable MFA with the Amplify CLI
Run amplify add auth to create a new Cognito Auth resource, and follow the prompts below depending on how you want to integrate MFA into your flow.
Turning MFA "ON" will make it required for all users, while "Optional" will make it available to enable on a per-user basis.
SMS MFA
$ amplify add auth
? Do you want to use the default authentication and security configuration? Manual configuration
# Answer as appropriate
? Multifactor authentication (MFA) user login options: ON (Required for all logins, can not be enabled later)? For user login, select the MFA types: SMS Text Message? Please specify an SMS authentication message: Your authentication code is {####}
# Answer as appropriate
Some next steps:"amplify push" will build all your local backend resources and provision it in the cloud"amplify publish" will build all your local backend and frontend resources (if you have hosting category added) and provision it in the cloudTOTP MFA
$ amplify add auth
? Do you want to use the default authentication and security configuration? Manual configuration
# Answer as appropriate
? Multifactor authentication (MFA) user login options: ON (Required for all logins, can not be enabled later)? For user login, select the MFA types: Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP)
# Answer as appropriate
Some next steps:"amplify push" will build all your local backend resources and provision it in the cloud"amplify publish" will build all your local backend and frontend resources (if you have hosting category added) and provision it in the cloudRun amplify update auth and follow the prompts as guided below.
The following steps show how to enable MFA as "Optional" for users. In this mode, MFA must be enabled on a user-by-user basis, either through an Admin SDK (e.g. via a Lambda trigger as part of the sign-up process), or manually in the Cognito console.
If you'd like to make MFA required for users, you must first delete your auth resource by running amplify remove auth, then follow the New Project flow on this page.
SMS MFA
$ amplify update auth
? What do you want to do? Walkthrough all the auth configurations
# Answer as appropriate
? Multifactor authentication (MFA) user login options: OPTIONAL (Individual users can use MFA)? For user login, select the MFA types: SMS Text Message? Please specify an SMS authentication message: Your authentication code is {####}
# Answer as appropriate
Some next steps:"amplify push" will build all your local backend resources and provision it in the cloud"amplify publish" will build all your local backend and frontend resources (if you have hosting category added) and provision it in the cloudTOTP MFA
$ amplify update auth
? What do you want to do? Walkthrough all the auth configurations
# Answer as appropriate
? Multifactor authentication (MFA) user login options: OPTIONAL (Individual users can use MFA)? For user login, select the MFA types: Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP)
# Answer as appropriate
Some next steps:"amplify push" will build all your local backend resources and provision it in the cloud"amplify publish" will build all your local backend and frontend resources (if you have hosting category added) and provision it in the cloudAfter you enable MFA you will also need to include MFA setup when users sign up. This will change depending on if you enable SMS, TOTP or both.
Multi-factor authentication with SMS
Once you have setup SMS as your second layer of authentication with MFA as shown above, your users will get an authentication code via a text message to complete sign-in after they sign in with their username and password.
If you do not have one already, you will need to configure an IAM role to use with Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) to manage SMS messages. You will then add this role under the "Messaging" tab for your user pool in the Amazon Cognito console. For additional information see the Amazon Cognito SMS text message MFA documentation.
Enable SMS MFA during sign-up
You will need to pass phone_number as a user attribute to enable SMS MFA for your users during sign-up. However, if the primary sign-in mechanism for your Cognito resource is phone_number (without enabling username), then you do not need to pass it as an attribute.
import { signUp } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignUp( username: string, password: string, phone_number: string, email: string) { try { await signUp({ username, password, options: { userAttributes: { phone_number, email } } }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { signUp } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignUp(username, password, phone_number, email) { try { await signUp({ username, password, options: { userAttributes: { phone_number, email } } }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}By default, you have to verify a user account after they sign up using the confirmSignUp API, which will send a one-time password to the user's phone number or email, depending on your Amazon Cognito configuration.
import { confirmSignUp } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignUpConfirmation( username: string, confirmationCode: string) { try { await confirmSignUp({ username, confirmationCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { confirmSignUp } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignUpConfirmation(username, confirmationCode) { try { await confirmSignUp({ username, confirmationCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Manage SMS MFA during sign-in
After a user signs in, if they have MFA enabled for their account, a challenge will be returned that you would need to call the confirmSignIn API where the user provides their confirmation code sent to their phone number.
import { signIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignIn(username: string, password: string) { try { await signIn({ username, password }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { signIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignIn(username, password) { try { await signIn({ username, password }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}If MFA is ON or enabled for the user, you must call confirmSignIn with the OTP sent to their phone.
import { confirmSignIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignInConfirmation(otpCode: string) { try { await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: otpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { confirmSignIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignInConfirmation(otpCode) { try { await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: otpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}After a user has been signed in, call updateMFAPreference to record the MFA type as enabled for the user and optionally set it as preferred so that subsequent logins default to using this MFA type.
import { updateMFAPreference } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleUpdateMFAPreference() { try { await updateMFAPreference({ sms: 'PREFERRED' }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Multi-factor authentication with TOTP
You can use Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) for multi-factor authentication (MFA) in your web or mobile applications. The Amplify Auth category includes support for TOTP setup and verification using authenticator apps, offering an integrated solution and enhanced security for your users. These apps, such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, have the TOTP algorithm built-in and work by using a shared secret key and the current time to generate short-lived, six digit passwords.
Set up TOTP for a user
After you initiate a user sign in with the signIn API where a user is required to set up TOTP as an MFA method, the API call will return CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_SETUP as a challenge and next step to handle in your app. You will get that challenge if the following conditions are met:
- MFA is marked as Required in your user pool.
- TOTP is enabled in your user pool.
- User does not have TOTP MFA set up already.
The CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_SETUP step signifies that the user must set up TOTP before they can sign in. The step returns an associated value of type TOTPSetupDetails which must be used to configure an authenticator app like Microsoft Authenticator or Google Authenticator. TOTPSetupDetails provides a helper method called getSetupURI which generates a URI that can be used, for example, in a button to open the user's installed authenticator app. For more advanced use cases, TOTPSetupDetails also contains a sharedSecret which can be used to either generate a QR code or be manually entered into an authenticator app.
Once the authenticator app is set up, the user can generate a TOTP code and provide it to the library to complete the sign in process.
import { signIn, SignInOutput } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignIn(username: string, password: string) { try { const output = await signIn({ username, password });
handleSignInNextSteps(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}
function handleSignInNextSteps(output: SignInOutput) { const { nextStep } = output; switch (nextStep.signInStep) { // ... case 'CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_SETUP': const totpSetupDetails = nextStep.totpSetupDetails; const appName = 'my_app_name'; const setupUri = totpSetupDetails.getSetupUri(appName); // Open setupUri with an authenticator APP to retrieve an OTP code break; // ... }}import { signIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignIn(username, password) { try { const output = await signIn({ username, password });
handleSignInNextSteps(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}
function handleSignInNextSteps(output) { const { nextStep } = output; switch (nextStep.signInStep) { // ... case 'CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_SETUP': const totpSetupDetails = nextStep.totpSetupDetails; const appName = 'my_app_name'; const setupUri = totpSetupDetails.getSetupUri(appName); // Open setupUri with an authenticator APP to retrieve an OTP code break; // ... }}The TOTP code can be obtained from the user via a text field or any other means. Once the user provides the TOTP code, call confirmSignIn with the TOTP code as the challengeResponse parameter.
import { confirmSignIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignInConfirmation(totpCode: string) { try { await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: totpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { confirmSignIn } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleSignInConfirmation(totpCode) { try { await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: totpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}After a user has been signed in, call updateMFAPreference to record the MFA type as enabled for the user and optionally set it as preferred so that subsequent logins default to using this MFA type.
import { updateMFAPreference } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleUpdateMFAPreference() { try { await updateMFAPreference({ totp: 'PREFERRED' }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Enable TOTP after a user is signed in
TOTP MFA can be set up after a user has signed in. This can be done when the following conditions are met:
- MFA is marked as Optional or Required in your user pool.
- TOTP is marked as an enabled MFA method in your user pool.
TOTP can be set up by calling the setUpTOTP and verifyTOTPSetup APIs in the Auth category.
Invoke the setUpTOTP API to generate a TOTPSetupDetails object which should be used to configure an Authenticator app like Microsoft Authenticator or Google Authenticator. TOTPSetupDetails provides a helper method called getSetupURI which generates a URI that can be used, for example, in a button to open the user's installed Authenticator app. For more advanced use cases, TOTPSetupDetails also contains a sharedSecret which can be used to either generate a QR code or be manually entered into an Authenticator app.
that contains the sharedSecret which will be used to either to generate a QR code or can be manually entered into an Authenticator app.
import { setUpTOTP } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleTOTPSetup() { try { const totpSetupDetails = await setUpTOTP(); const appName = 'my_app_name'; const setupUri = totpSetupDetails.getSetupUri(appName); // Open setupUri with an authenticator APP to retrieve an OTP code } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Once the Authenticator app is set up, the user must generate a TOTP code and provide it to the library. Pass the code to verifyTOTPSetup to complete the TOTP setup process.
import { verifyTOTPSetup } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleTOTPVerification(totpCode: string) { try { await verifyTOTPSetup({ code: totpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { verifyTOTPSetup } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleTOTPVerification(totpCode) { try { await verifyTOTPSetup({ code: totpCode }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}After TOTP setup is complete, call updateMFAPreference to record the MFA type as enabled for the user and optionally set it as preferred so that subsequent logins default to using this MFA type.
import { updateMFAPreference } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleUpdateMFAPreference() { try { await updateMFAPreference({ sms: 'ENABLED', totp: 'PREFERRED' }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Recover from a lost TOTP device
In a scenario where MFA is marked as "Required" in the Cognito User Pool and another MFA method is not set up, the administrator would need to first initiate an AdminUpdateUserAttributes call and update the user’s phone number attribute. Once this is complete, the administrator can continue changing the MFA preference to SMS as suggested above.
Set up a user's preferred MFA method
Fetch the current user's MFA preferences
Invoke the following API to get the current MFA preference and enabled MFA types, if any, for the current user.
import { fetchMFAPreference } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleFetchMFAPreference() { try { const output = await fetchMFAPreference(); console.log(`Enabled MFA types for the user: ${output.enabled}`); console.log(`Preferred MFA type for the user: ${output.preferred}`); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Update the current user's MFA preferences
Invoke the following API to update the MFA preference for the current user.
import { updateMFAPreference } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleUpdateMFAPreference() { try { await updateMFAPreference({ sms: 'ENABLED', totp: 'PREFERRED' }); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}If multiple MFA methods are enabled for the user, the signIn API will return CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_MFA_SELECTION as the next step in the auth flow. During this scenario, the user should be prompted to select the MFA method they want to use to sign in and their preference should be passed to confirmSignIn.
import { confirmSignIn, SignInOutput } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
function handleSignInNextSteps(output: SignInOutput) { const { nextStep } = output; switch (nextStep.signInStep) { // ... case 'CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_MFA_SELECTION': const allowedMFATypes = nextStep.allowedMFATypes; const mfaType = promptUserForMFAType(allowedMFATypes); case 'CONFIRM_SIGN_IN_WITH_SMS_CODE': // display user to enter otp code; break; case 'CONFIRM_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_CODE': // display user to enter otp code; break; // ... }}
function promptUserForMFAType( allowedMFATypes?: ('SMS' | 'TOTP')[]): 'SMS' | 'TOTP' { // Prompt user to select MFA type}
async function handleMFASelection(mfaType: 'SMS' | 'TOTP') { try { const output = await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: mfaType }); handleSignInNextSteps(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}function handleSignInNextSteps(output) { const { nextStep } = output; switch (nextStep.signInStep) { // ... case 'CONTINUE_SIGN_IN_WITH_MFA_SELECTION': const allowedMFATypes = nextStep.allowedMFATypes; const mfaType = promptUserForMFAType(allowedMFATypes); case 'CONFIRM_SIGN_IN_WITH_SMS_CODE': // display user to enter otp code; break; case 'CONFIRM_SIGN_IN_WITH_TOTP_CODE': // display user to enter otp code; break; // ... }}
function promptUserForMFAType(allowedMFATypes) { // Prompt user to select MFA type}
async function handleMFASelection(mfaType) { try { const output = await confirmSignIn({ challengeResponse: mfaType }); handleSignInNextSteps(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Remember a device
Remembering a device is useful in conjunction with MFA because it allows the second factor requirement to be automatically met when your user signs in on that device and reduces friction in their sign-in experience.
Configure device tracking
You can enable the remembered device functionality in the Cognito User Pool console. To begin, go to your project directory and issue the command:
amplify auth consoleSelect the following option to open the Cognito User Pool console:
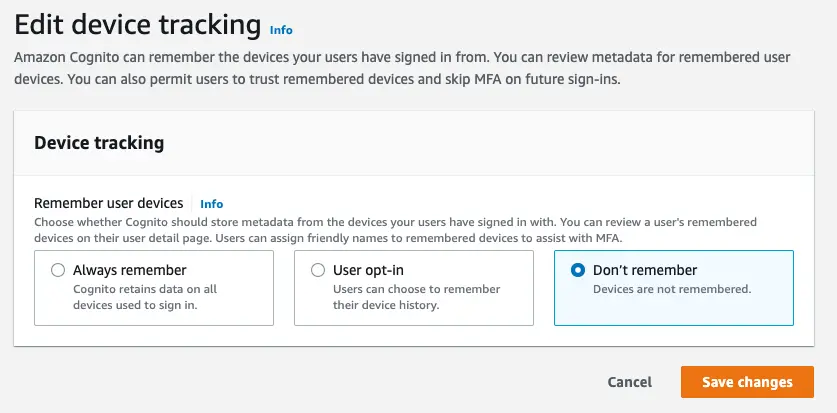
? Which Console User PoolWhen the console opens, scroll down to the "Device Tracking" section and select the "Edit" button. This will render the following page allowing you to configure your preference for remembering a user's device.
Choose either "Always remember" to remember a user's device by default or "User Opt-in" to give the user the ability to choose.
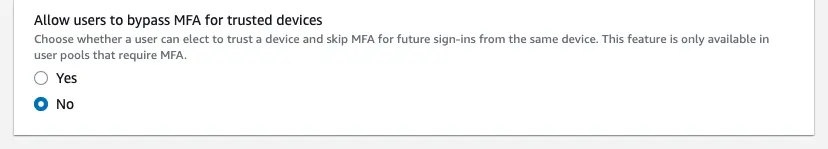
When MFA is enabled you will have the option to suppress the second factor during multi-factor authentication. Choose "Yes" if you want a remembered device to be used as a second factor mechanism.
When you have made your selection(s), click "Save changes". You are now ready to start updating your code to manage remembered devices.
Learn moreUnderstand key terms used for tracking devices
There are differences to keep in mind when working with remembered, forgotten, and tracked devices.
- Tracked: Every time the user signs in with a new device, the client is given the device key at the end of a successful authentication event. We use this device key to generate a salt and password verifier which is used to call the
ConfirmDeviceAPI. At this point, the device is considered to be "tracked". Once the device is in a tracked state, you can use the Amazon Cognito console to see the time it started to be tracked, last authentication time, and other information about that device. - Remembered: Remembered devices are also tracked. During user authentication, the device key and secret pair assigned to a remembered device is used to authenticate the device to verify that it is the same device that the user previously used to sign in.
- Not Remembered: A not-remembered device is a tracked device where Cognito has been configured to require users to "Opt-in" to remember a device but the user has chosen not to remember the device. This use case is for users signing into their application from a device that they don't own.
- Forgotten: In the event that you no longer want to remember or track devices, you can use the
forgetDevice()API to remove devices from being both remembered and tracked.
Remember devices
You can remember devices using the following:
import { rememberDevice } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
export async function handleRememberDevice() { try { await rememberDevice(); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { rememberDevice } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
export async function handleRememberDevice() { try { await rememberDevice(); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Forget devices
You can also forget devices but note that forgotten devices are neither remembered nor tracked.
import { forgetDevice } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
export async function handleForgetDevice() { try { await forgetDevice(); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { forgetDevice } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
export async function handleForgetDevice() { try { await forgetDevice(); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}Fetch devices
You can fetch a list of remembered devices by using the following:
import { fetchDevices } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
export async function handleFetchDevices() { try { const output = await fetchDevices(); console.log(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}import { fetchDevices } from 'aws-amplify/auth';
async function handleFetchDevices() { try { const output = await Auth.fetchDevices(); console.log(output); } catch (error) { console.log(error); }}You can now set up devices to be remembered, forgotten, and fetched.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You finished the Manage MFA settings guide. In this guide, you set up and configured MFA for your users and provided them options on remembering their MFA preferences and devices.
Next steps
Now that you completed setting up multi-factor authentication you may also want to add additional customization. We recommend you learn more about: