Upload files
Upload File
To upload to S3 from a file, specify the path to upload the file to and the localFile to be uploaded. localFile can be an instance of AWSFile created from either an OS platform File instance or the result of Flutter file picker plugins such as file_picker.
Upload platform File
import 'package:amplify_flutter/amplify_flutter.dart';
Future<void> uploadFile() async { try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFile.fromPath('/path/to/local/file.txt'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/file.txt'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded file: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}import 'dart:io' show File;
import 'package:amplify_flutter/amplify_flutter.dart';import 'package:aws_common/vm.dart';
Future<void> uploadFile(File file) async { try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFilePlatform.fromFile(file), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/file.png'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded file: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}import 'dart:html' show File;
import 'package:amplify_flutter/amplify_flutter.dart';import 'package:aws_common/web.dart';
Future<void> uploadFile(File file) async { final awsFile = AWSFilePlatform.fromFile(file); try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: awsFile, path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/file.png'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded file: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}Upload with Flutter file_picker plugin
The file_picker plugin can be used to retrieve arbitrary file types from the user's device.
import 'package:amplify_flutter/amplify_flutter.dart';import 'package:file_picker/file_picker.dart';
Future<void> uploadImage() async { // Select a file from the device final result = await FilePicker.platform.pickFiles( type: FileType.custom, withData: false, // Ensure to get file stream for better performance withReadStream: true, allowedExtensions: ['jpg', 'png', 'gif'], );
if (result == null) { safePrint('No file selected'); return; }
// Upload file using the filename final platformFile = result.files.single; try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFile.fromStream( platformFile.readStream!, size: platformFile.size, ), path: StoragePath.fromString('public/${platformFile.name}'), onProgress: (progress) { safePrint('Fraction completed: ${progress.fractionCompleted}'); }, ).result; safePrint('Successfully uploaded file: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}Upload Data
To upload to S3 from a data object, specify the path to upload the file to and the data to upload. data should be an instance of StorageDataPayload created from various data formats.
Future<void> uploadData() async { try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.string( 'hello world', contentType: 'text/plain', ), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded data: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}Future<void> uploadData() async { try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.json({ 'title': 'example', 'author': { 'firstName': 'Jane', 'lastName': 'Doe', }, }), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.json'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded data: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}StorageDataPayload.dataUrl() parses the provided data URL string, and throws exception if the data URL is invalid. See more info about data URL.
Future<void> uploadData() async { const dataUrl = 'data:text/plain;charset=utf-8;base64,aGVsbG8gd29ybGQ='; try { final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.dataUrl(dataUrl), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded data: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}Future<void> uploadBytes() async { try { final bytes = 'hello world'.codeUnits; final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.bytes( bytes, contentType: 'text/plain', ), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), ).result; safePrint('Uploaded data: ${result.uploadedItem.path}'); } on StorageException catch (e) { safePrint(e.message); }}Upload Progress
To track progress of the upload, use the progress listener callback.
final operation = Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFile.fromPath('/path/to/local/file.txt'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), onProgress: (progress) { safePrint('fraction totalBytes: ${progress.totalBytes}'); safePrint('fraction transferredBytes: ${progress.transferredBytes}'); safePrint('fraction completed: ${progress.fractionCompleted}'); });final operation = Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.string('hello world'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), onProgress: (progress) { safePrint('fraction totalBytes: ${progress.totalBytes}'); safePrint('fraction transferredBytes: ${progress.transferredBytes}'); safePrint('fraction completed: ${progress.fractionCompleted}'); },);Upload Options
You can attach metadata while uploading data or a file by specifying the metadata property in options. If you want the metadata to be included in the upload result, you can set the getProperties flag to true in options.
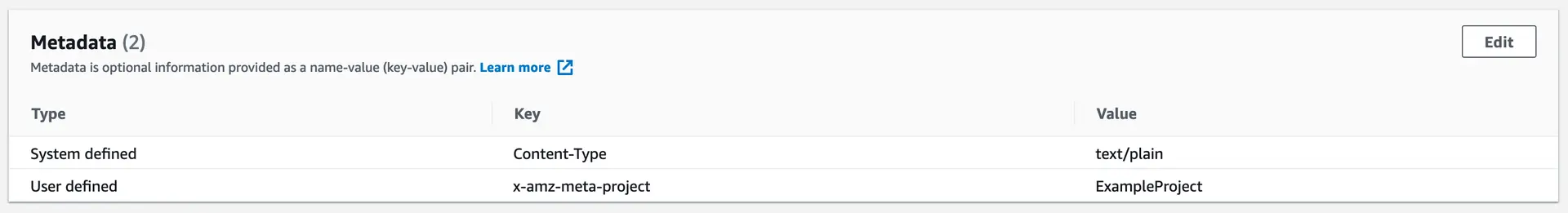
final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFile.fromPath('/path/to/local/file.txt'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), options: const StorageUploadFileOptions( metadata: {'key': 'value'}, pluginOptions: S3UploadFilePluginOptions( getProperties: true, ), ),).resultsafePrint('metadata: ${result.uploadedItem.metadata}');final result = await Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.string('example'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), options: const StorageUploadDataOptions( metadata: {'key': 'value'}, pluginOptions: S3UploadDataPluginOptions( getProperties: true, ), ),).result;safePrint('metadata: ${result.uploadedItem.metadata}');The Amplify.Storage.getProperties API allows you to retrieve metadata without downloading the file.
In S3 console, you should see the metadata attached to your file as the following.
Control of Upload Operations
A call to Amplify.Storage.uploadFile or Amplify.Storage.uploadData returns a reference to the operation that is performing the upload.
To cancel the upload (for example, in response to the user pressing a Cancel button), simply call .cancel() on the returned upload operation.
Amplify.Storage.uploadFile also allows for the operation to be paused and resumed.
Future<void> upload() async { final operation = Amplify.Storage.uploadFile( localFile: AWSFile.fromPath('/path/to/local/file.txt'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), );
// pause operation await operation.pause();
// resume operation await operation.resume();
// cancel operation await operation.cancel();}Future<void> upload() async { final operation = Amplify.Storage.uploadData( data: StorageDataPayload.string('example'), path: const StoragePath.fromString('public/example.txt'), );
// cancel operation await operation.cancel();}Multipart Upload
Amplify will automatically perform a S3 multipart upload for files larger than 5MB. For more information about S3's multipart upload support, see Uploading and copying objects using multipart upload.