Connect to external Amazon DynamoDB data sources
The a.model() data model allows you to define a GraphQL schema for an AWS AppSync API where models are backed by DynamoDB Tables managed by Amplify. The generated schema also provides queries and mutations to the Amplify Data client. However, you may want to connect to an external DynamoDB table and execute custom business logic against it instead.
In the following sections, we walk through the steps to add and use an external DynamoDB table as a data source for your API:
- Set up your Amazon DynamoDB table
- Add your Amazon DynamoDB table as a data source
- Define custom queries and mutations
- Configure custom business logic handler code
- Invoke custom queries or mutations
Step 1 - Set up your Amazon DynamoDB table
For the purpose of this guide we will define a Post type and create an external DynamoDB table that will store records for it. In Amplify Gen 2, customType adds a type to the schema that is not backed by an Amplify-generated DynamoDB table.
With the Post type defined, it can then be referenced as the return type when defining your custom queries and mutations.
First, add the Post custom type to your schema:
import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Todo: a .model({ content: a.string(), }) .authorization(allow => [allow.publicApiKey()]), Post: a.customType({ id: a.id().required(), author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), ups: a.integer(), downs: a.integer(), version: a.integer(), }),});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: 'apiKey', apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});Once the deployment successfully completes, navigate to the AppSync console and select your Amplify-generated API. Follow these steps to create a new DynamoDB table:
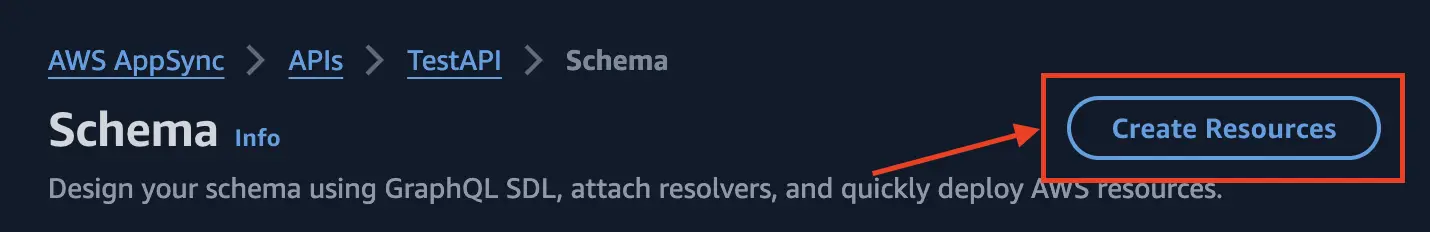
- On the Schema page, choose Create Resources.
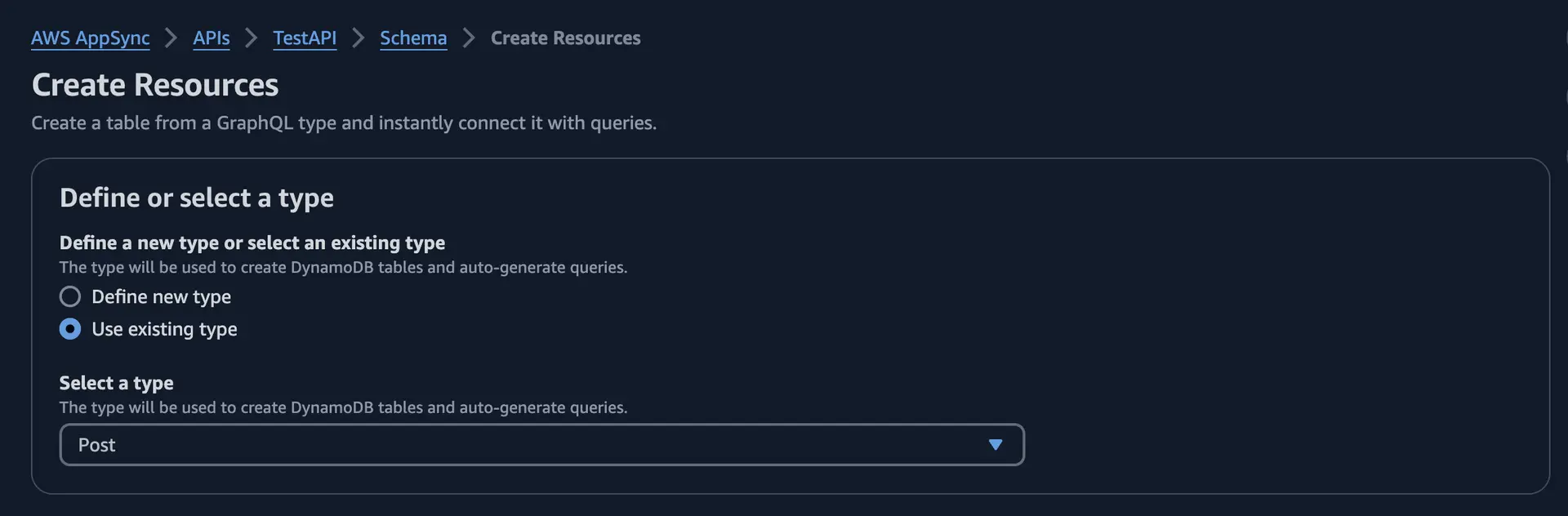
- Choose Use existing type, then choose the Post type.
-
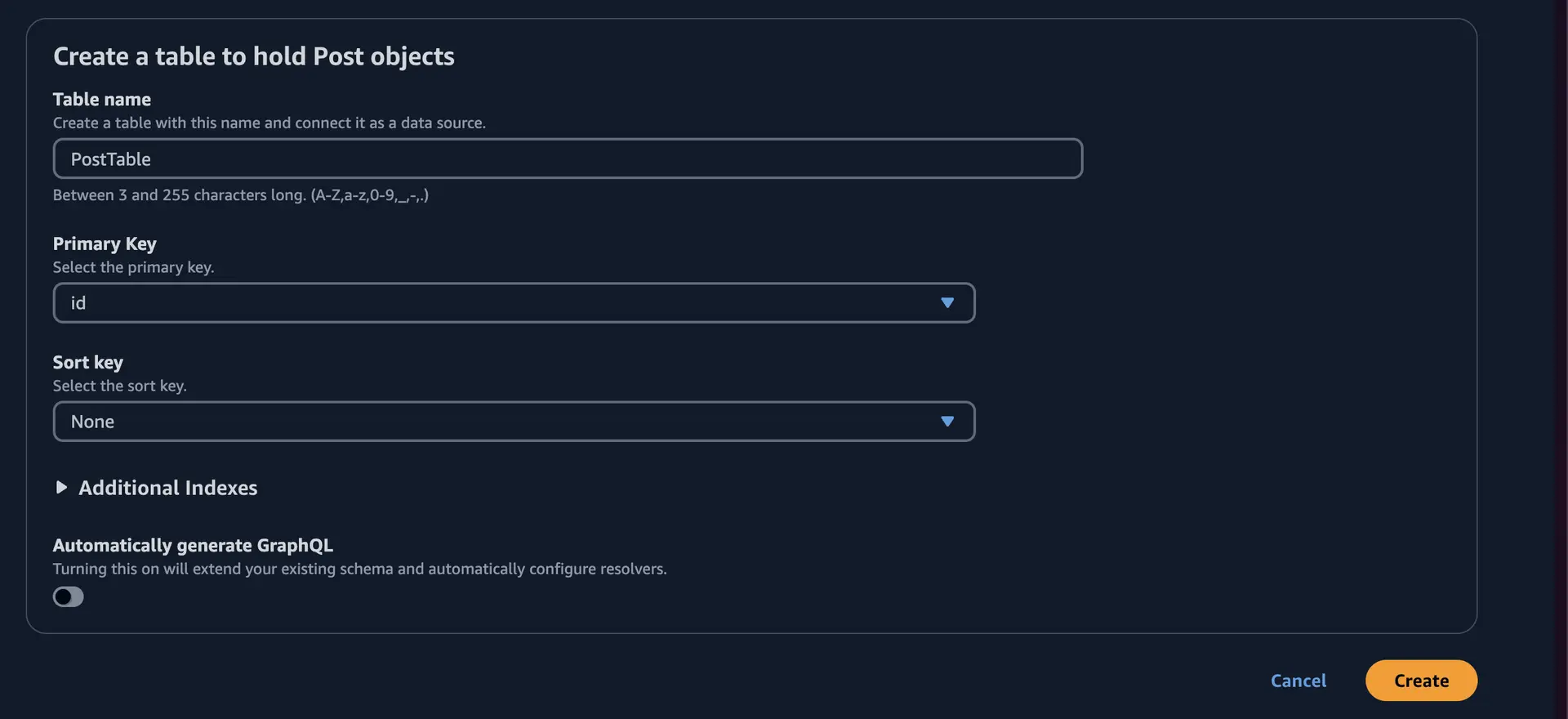
Set the Primary key to
idand the Sort key toNone. -
Disable Automatically generate GraphQL. In this example, we'll create the resolver ourselves.
- Choose Create.
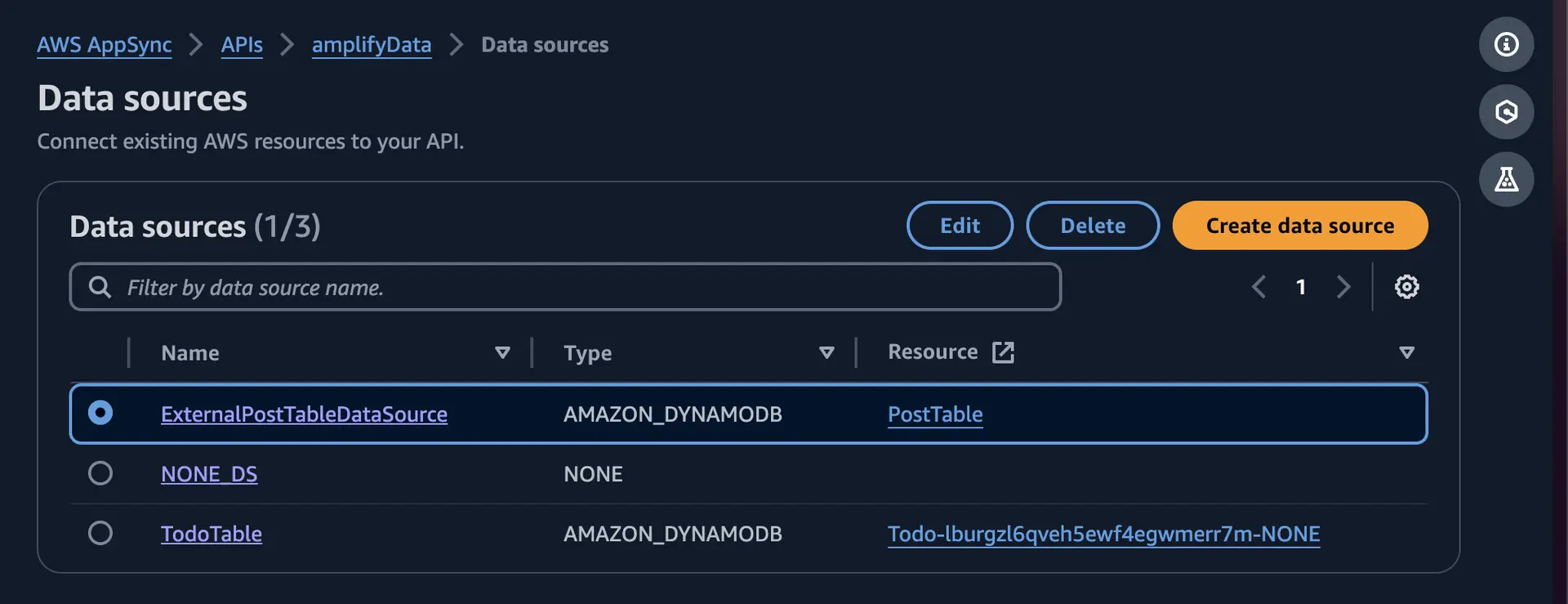
You now have a new DynamoDB table named PostTable, which you can see by visiting Data sources in the side tab. You will use this table as the data source for your custom queries and mutations to your Amazon DynamoDB table.
Step 2 - Add your Amazon DynamoDB table as a data source
In your amplify/backend.ts file, add your DynamoDB table as a data source for your API:
import { defineBackend } from "@aws-amplify/backend";import { auth } from "./auth/resource";import { data } from "./data/resource";import { aws_dynamodb } from "aws-cdk-lib";
export const backend = defineBackend({ auth, data,});
const externalDataSourcesStack = backend.createStack("MyExternalDataSources");
const externalTable = aws_dynamodb.Table.fromTableName( externalDataSourcesStack, "MyExternalPostTable", "PostTable");
backend.data.addDynamoDbDataSource( "ExternalPostTableDataSource", externalTable);Step 3 - Define custom queries and mutations
Now that your DynamoDB table has been added as a data source, you can reference it in custom queries and mutations using the a.handler.custom() modifier which accepts the name of the data source and an entry point for your resolvers.
Use the following code examples to add addPost, getPost, updatePost, and deletePost as custom queries and mutations to your schema:
import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Post: a.customType({ author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), ups: a.integer(), downs: a.integer(), version: a.integer(), }), addPost: a .mutation() .arguments({ id: a.id(), author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), }) .returns(a.ref("Post")) .authorization(allow => [allow.publicApiKey()]) .handler( a.handler.custom({ dataSource: "ExternalPostTableDataSource", entry: "./addPost.js", }) ),});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: 'apiKey', apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Post: a.customType({ author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), ups: a.integer(), downs: a.integer(), version: a.integer(), }), getPost: a .query() .arguments({ id: a.id().required() }) .returns(a.ref("Post")) .authorization(allow => [allow.publicApiKey()]) .handler( a.handler.custom({ dataSource: "ExternalPostTableDataSource", entry: "./getPost.js", }) ),});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: 'apiKey', apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Post: a.customType({ author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), ups: a.integer(), downs: a.integer(), version: a.integer(), }), updatePost: a .mutation() .arguments({ id: a.id().required(), author: a.string(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), expectedVersion: a.integer().required(), }) .returns(a.ref("Post")) .authorization(allow => [allow.publicApiKey()]) .handler( a.handler.custom({ dataSource: "ExternalPostTableDataSource", entry: "./updatePost.js", }) ),});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: 'apiKey', apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});import { type ClientSchema, a, defineData } from "@aws-amplify/backend";
const schema = a.schema({ Post: a.customType({ author: a.string().required(), title: a.string(), content: a.string(), url: a.string(), ups: a.integer(), downs: a.integer(), version: a.integer(), }), deletePost: a .mutation() .arguments({ id: a.id().required(), expectedVersion: a.integer() }) .returns(a.ref("Post")) .authorization(allow => [allow.publicApiKey()]) .handler( a.handler.custom({ dataSource: "ExternalPostTableDataSource", entry: "./deletePost.js", }) ),});
export type Schema = ClientSchema<typeof schema>;
export const data = defineData({ schema, authorizationModes: { defaultAuthorizationMode: 'apiKey', apiKeyAuthorizationMode: { expiresInDays: 30, }, },});Step 4 - Configure custom business logic handler code
Next, create the following files in your amplify/data folder and use the code examples to define custom resolvers for the custom queries and mutations added to your schema from the previous step. These are AppSync JavaScript resolvers
import { util } from "@aws-appsync/utils";import * as ddb from "@aws-appsync/utils/dynamodb";
export function request(ctx) { const item = { ...ctx.arguments, ups: 1, downs: 0, version: 1 }; const key = { id: ctx.args.id ?? util.autoId() }; return ddb.put({ key, item });}
export function response(ctx) { return ctx.result;}import * as ddb from "@aws-appsync/utils/dynamodb";
export function request(ctx) { return ddb.get({ key: { id: ctx.args.id } });}
export const response = (ctx) => ctx.result;import { util } from "@aws-appsync/utils";import * as ddb from "@aws-appsync/utils/dynamodb";
export function request(ctx) { const { id, expectedVersion, ...rest } = ctx.args; const values = Object.entries(rest).reduce((obj, [key, value]) => { obj[key] = value ?? ddb.operations.remove(); return obj; }, {});
return ddb.update({ key: { id }, condition: { version: { eq: expectedVersion } }, update: { ...values, version: ddb.operations.increment(1) }, });}
export function response(ctx) { const { error, result } = ctx; if (error) { util.appendError(error.message, error.type); } return result;}import { util } from "@aws-appsync/utils";import * as ddb from "@aws-appsync/utils/dynamodb";
export function request(ctx) { let condition = null; if (ctx.args.expectedVersion) { condition = { or: [ { id: { attributeExists: false } }, { version: { eq: ctx.args.expectedVersion } }, ], }; } return ddb.remove({ key: { id: ctx.args.id }, condition });}
export function response(ctx) { const { error, result } = ctx; if (error) { util.appendError(error.message, error.type); } return result;}Step 5 - Invoke custom queries or mutations
From your generated Data client, you can find all your custom queries and mutations under the client.queries. and client.mutations. APIs respectively.
const { data, errors } = await client.mutations.addPost({ title: "My Post", content: "My Content", author: "Chris",});const { data, errors } = await client.queries.getPost({ id: "<post-id>"});const { data, errors } = await client.mutations.updatePost({ id: "<post-id>", title: "An Updated Post", expectedVersion: 1,});const { data, errors } = await client.mutations.deletePost({ id: "<post-id>",});Conclusion
In this guide, you’ve added an external DynamoDB table as a data source to an Amplify GraphQL API and defined custom queries and mutations, handled by AppSync JS resolvers, to manipulate Post items in an external DynamoDB table using the Amplify Gen 2 Data client.
To clean up, you can delete your sandbox by accepting the prompt when terminating the sandbox process in your terminal. Alternatively, you can also use the AWS Amplify console to manage and delete sandbox environments.
To delete your external DynamoDB table, you can navigate to the AppSync console and click on the name of the table in the data sources list. This takes you to the DynamoDB console where you can delete the table.
All DynamoDB operations & example resolvers
GetItem
Reference - The GetItem request lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a GetItem request to DynamoDB, and enables you to specify:
- The key of the item in DynamoDB
- Whether to use a consistent read or not
Example:
export function request(ctx) { const { foo, bar } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'GetItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ foo, bar }), consistentRead: true };}PutItem
PutItem - The PutItem request mapping document lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a PutItem request to DynamoDB, and enables you to specify the following:
- The key of the item in DynamoDB
- The full contents of the item (composed of key and attributeValues)
- Conditions for the operation to succeed
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { foo, bar, ...values } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'PutItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ foo, bar }), attributeValues: util.dynamodb.toMapValues(values) };}UpdateItem
UpdateItem - The UpdateItem request enables you to tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a UpdateItem request to DynamoDB and allows you to specify the following:
- The key of the item in DynamoDB
- An update expression describing how to update the item in DynamoDB
- Conditions for the operation to succeed
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { id } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'UpdateItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ id }), update: { expression: 'ADD #voteField :plusOne, version :plusOne', expressionNames: { '#voteField': 'upvotes' }, expressionValues: { ':plusOne': { N: 1 } } } };}DeleteItem
DeleteItem - The DeleteItem request lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a DeleteItem request to DynamoDB, and enables you to specify the following:
- The key of the item in DynamoDB
- Conditions for the operation to succeed
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { return { operation: 'DeleteItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ id: ctx.args.id }) };}Query
Query - The Query request object lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB resolver to make a Query request to DynamoDB, and enables you to specify the following:
- Key expression
- Which index to use
- Any additional filter
- How many items to return
- Whether to use consistent reads
- query direction (forward or backward)
- Pagination token
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { owner } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'Query', query: { expression: 'ownerId = :ownerId', expressionValues: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ ':ownerId': owner }) }, index: 'owner-index' };}Scan
Scan - The Scan request lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a Scan request to DynamoDB, and enables you to specify the following:
- A filter to exclude results
- Which index to use
- How many items to return
- Whether to use consistent reads
- Pagination token
- Parallel scans
Example:
export function request(ctx) { return { operation: 'Scan' };}Sync
Sync - The Sync request object lets you retrieve all the results from a DynamoDB table and then receive only the data altered since your last query (the delta updates). Sync requests can only be made to versioned DynamoDB data sources. You can specify the following:
-
A filter to exclude results
-
How many items to return
-
Pagination Token
-
When your last Sync operation was started
Example:
export function request(ctx) { const { nextToken, lastSync } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'Sync', limit: 100, nextToken, lastSync };}BatchGetItem
BatchGetItem - The BatchGetItem request object lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a BatchGetItem request to DynamoDB to retrieve multiple items, potentially across multiple tables. For this request object, you must specify the following:
-
The table names where to retrieve the items from
-
The keys of the items to retrieve from each table
The DynamoDB BatchGetItem limits apply and no condition expression can be provided.
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { authorId, postId } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'BatchGetItem', tables: { authors: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId })], posts: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId, postId })], }, };}BatchDeleteItem
BatchDeleteItem - The BatchDeleteItem request object lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a BatchWriteItem request to DynamoDB to delete multiple items, potentially across multiple tables. For this request object, you must specify the following:
-
The table names where to delete the items from
-
The keys of the items to delete from each table
The DynamoDB BatchWriteItem limits apply and no condition expression can be provided.
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { authorId, postId } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'BatchDeleteItem', tables: { authors: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId })], posts: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId, postId })], }, };}BatchPutItem
BatchPutItem - The BatchPutItem request object lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a BatchWriteItem request to DynamoDB to put multiple items, potentially across multiple tables. For this request object, you must specify the following:
-
The table names where to put the items in
-
The full items to put in each table
The DynamoDB BatchWriteItem limits apply and no condition expression can be provided.
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { authorId, postId, name, title } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'BatchPutItem', tables: { authors: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId, name })], posts: [util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId, postId, title })], }, };}TransactGetItems
TransactGetItems - The TransactGetItems request object lets you to tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a TransactGetItems request to DynamoDB to retrieve multiple items, potentially across multiple tables. For this request object, you must specify the following:
-
The table name of each request item where to retrieve the item from
-
The key of each request item to retrieve from each table
The DynamoDB TransactGetItems limits apply and no condition expression can be provided.
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { authorId, postId } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'TransactGetItems', transactItems: [ { table: 'posts', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ postId }), }, { table: 'authors', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId }), }, ], };}TransactWriteItems
TransactWriteItems - The TransactWriteItems request object lets you tell the AWS AppSync DynamoDB function to make a TransactWriteItems request to DynamoDB to write multiple items, potentially to multiple tables. For this request object, you must specify the following:
-
The destination table name of each request item
-
The operation of each request item to perform. There are four types of operations that are supported:
PutItem,UpdateItem,DeleteItem, andConditionCheck -
The key of each request item to write
The DynamoDB TransactWriteItems limits apply.
Example:
import { util } from '@aws-appsync/utils';
export function request(ctx) { const { authorId, postId, title, description, oldTitle, authorName } = ctx.args; return { operation: 'TransactWriteItems', transactItems: [ { table: 'posts', operation: 'PutItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ postId }), attributeValues: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ title, description }), condition: util.transform.toDynamoDBConditionExpression({ title: { eq: oldTitle }, }), }, { table: 'authors', operation: 'UpdateItem', key: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ authorId }), update: { expression: 'SET authorName = :name', expressionValues: util.dynamodb.toMapValues({ ':name': authorName }), }, }, ], };}